Python:自分用メモ
最終更新:2024 年 11 月 29 日
自分が実験などで解析に使う Python コードをまとめたものです。
数値積分
実装
台形公式を用いて計算します。
integral.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data1 = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 101)
data2 = np.sin(data1) + 1
# プロット
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(data1, data2)
ax.grid()
plt.show()
# 数値積分(台形公式)
dif = data1[1] - data1[0]
print("計算値", (np.sum(data2[:-1]) + np.sum(data2[1:])) * dif/2)
print("理論値", np.pi * 2)
結果
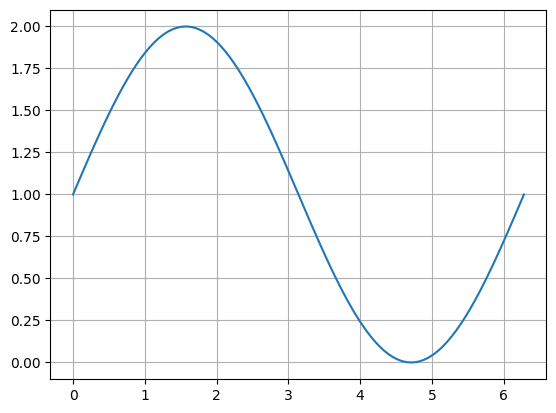
計算値 6.283185307179587
理論値 6.283185307179586
であり、計算値と理論値とは、 程度のオーダーで一致した。
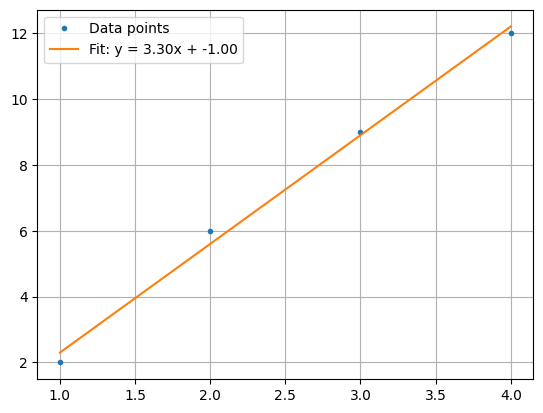
最小二乗法
実装
numpy.polyfitを使うようです。
least_squares.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_axis = [1, 2, 3, 4]
y_axis = [2, 6, 9, 12]
# 最小二乗法による直線当てはめ
slope, intercept = np.polyfit(x_axis, y_axis, 1)
# 回帰直線のy座標を計算
fit_line = np.array(x_axis) * slope + intercept
# プロット
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x_axis, y_axis, ".", label="Data points")
ax.plot(x_axis, fit_line, "-", label=f"Fit: y = {slope:.2f}x + {intercept:.2f}")
ax.grid()
ax.legend()
plt.show()
結果
に線形回帰される。
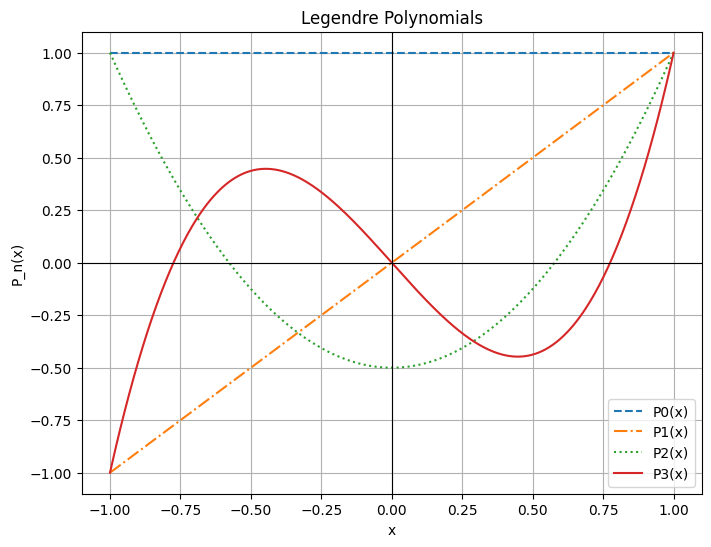
ルジャンドル多項式
実装
numpy.polynomial.legendre を使うようです。
legendre.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from numpy.polynomial.legendre import Legendre
# x軸の範囲を設定
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 500)
# ルジャンドル多項式を定義
P0 = Legendre([1]) # P0(x)
P1 = Legendre([0, 1]) # P1(x)
P2 = Legendre([0, 0, 1]) # P2(x)
P3 = Legendre([0, 0, 0, 1]) # P3(x)
# グラフを描画
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(x, P0(x), label="P0(x)", linestyle="--")
plt.plot(x, P1(x), label="P1(x)", linestyle="-.")
plt.plot(x, P2(x), label="P2(x)", linestyle=":")
plt.plot(x, P3(x), label="P3(x)")
# グラフの外形を強調
plt.axhline(0, color='black', linewidth=0.8) # x軸
plt.axvline(0, color='black', linewidth=0.8) # y軸
# ラベルと凡例
plt.title("Legendre Polynomials")
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("P_n(x)")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
結果
0 次、1 次、2 次、3 次のルジャンドル多項式は
であり、次のように表せる。